We live in a world where more and more people are opting for a vegan diet and / or without animal products. This has been a great challenge when it comes to confectionery. Why? Because there are components in sweet recipes that are of animal origin and that fulfil important technical functions.
or this reason, it is important to have the necessary knowledge of how these products can be replaced. The reason is that we consider it essential not to give up either textures or flavours. In this way, we will continue to create all the types of pastry that people want to eat, even if they contain other ingredients.
This time we will talk about dairy products and their substitution. Dairy products in pastry recipes provide creaminess, texture and flavor. To replace them with products of vegetable origin there are certain parameters that must be taken into account if we want to obtain stable and perfectly balanced textures.
Below, we analyze their composition and propose some substitution methods.
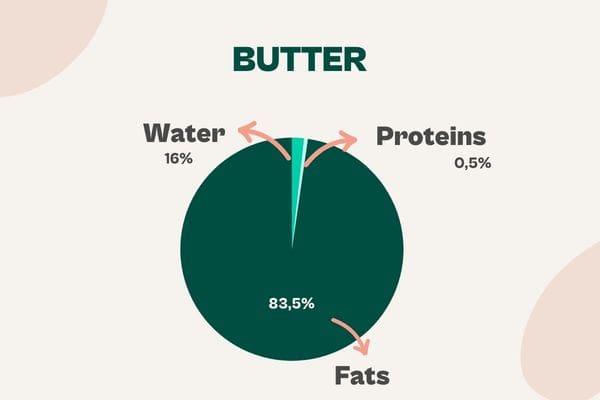
Butter
Butter fulfills the technical functions of fat, texture and emulsion, in addition to flavor.
As far as taste is concerned, we believe that this is a dispensable feature in a vegetable bakery, but it is important not to renounce its technical functions.
Plant-based alternatives
There are lots of butter substitutes on the market, but their composition varies depending on the manufacturer in terms of the fats, flavour, colour and even technical characteristics they include.
This is why we recommend our own plant-based substitutes, both of which have a neutral flavour but different textures to suit their intended use:
- Layered pastries (for example puff) or recipes where the texture needs to be more solid.
- General use.

Ingredientes
-
- 150g – Water
- 580g – Deodorized coconut fat
- 250g – Sunflower oil
- 10g – Natur Emul
- 12g – Sojawhip
Elaboración
-
- Blend the water with the Sojawhip and Natur Emul with an electric mixer until a homogeneous mixture is obtained.
- Melt the coconut fat and mix it with the sunflower oil. The temperature of the oil mixture should be 18/20 °C.
- Add the oils little by little in the first preparation and emulsify with an electric mixer.
- If the emulsion breaks, it means that the temperature of the mixture has risen too high. In this case, cool until it starts to crystallize and emulsify again.
- The final result should be like a dense mayonnaise. Keep in the refrigerator, where it will crystallize and harden.

Ingredientes
-
- 150g – Water
- 300g – Deodorized coconut fat
- 300g – Shea butter
- 250g – Sunflower oil
- 10g – Natur Emul
- 12g – Sojawhip
Elaboración
-
- Blend the water with the soy protein. Add the Natur Emul and grind again until a homogeneous mixture is obtained.
- Melt the coconut fat and shea butter and add them to the sunflower oil. The temperature of the oil mixture should be approximately 20 °C.
- Add the oils little by little to the first preparation and emulsify.
- If the emulsion breaks, it means that the temperature of the mixture has risen too high. In this case, cool until it starts to crystallize and emulsify again.
- The final result should be like a dense mayonnaise. In the refrigerator it will crystallize and harden.
Milk
In pastry-making, milk adds water, flavour, cream and emulsifying properties. In fact, milk is a stable emulsion itself.
However, it’s also an easy product to replace with a plant-based alternative such as plant-based drinks, for instance, which are easy to buy or even make in your own kitchen.
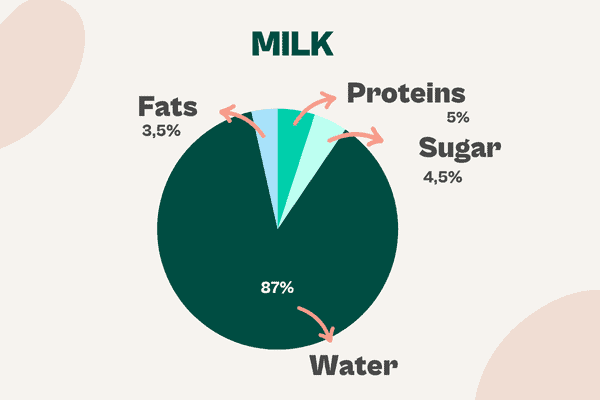
These liquids are also rich in protein, so you don’t lose any of the milk’s emulsifying qualities. These plant-based drinks are also rich in protein so that the emulsifying function of milk is not lost. They include: soy drink, rice drink, oat drink, almond drink, hazelnut drink, coconut drink.
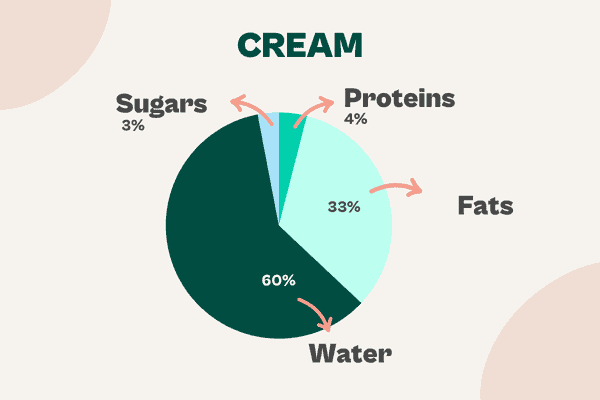
Cream
Cream is more complicated than milk, because it has all the technical functions of milk but it also adds air and fat.
If you are making a mousse, for instance, you can switch the aerating function of the cream for a meringue mix made with Potatowhip / Potatowhip Cold or Sojawhip. You can also use alternative fats such as coconut fat or cocoa or shea butter, or flavoured fats like nut pastes or chocolate.
Plant-based alternatives


In conclusion, the evolution towards an inclusive pastry that respects the dietary preferences of each individual is not only possible, but also exciting. We have explored how dairy products, the mainstay of traditional pastry making, can be effectively replaced by plant-based alternatives without sacrificing the texture, taste or quality of our creations. Remember that our complete Plant-based Pastry-making Indispensable Dossier is available for those who wish to delve deeper into this fascinating world of possibilities.









 938 666 094
938 666 094
 sosa@sosa.cat
sosa@sosa.cat